A/B/n testing, also known as split testing or bucket testing, is a method of comparing two or more variations of a product or website to determine which one performs better. It is commonly used in fields such as marketing, product development, and user experience (UX) design to make data-driven decisions about how to optimize a product for maximum engagement or conversion. The “A” and “B” in A/B testing refer to the two variations being compared, while “n” is used to indicate more than two variations.
A/B/n testing works by randomly showing users one of the variations (A, B, or n) and then measuring their engagement or conversion rate. This is done by using a control group, which is shown the original version of the product or website, and an experimental group, which is shown the variation being tested. The engagement or conversion rate is then compared between the two groups to determine which variation performs better.
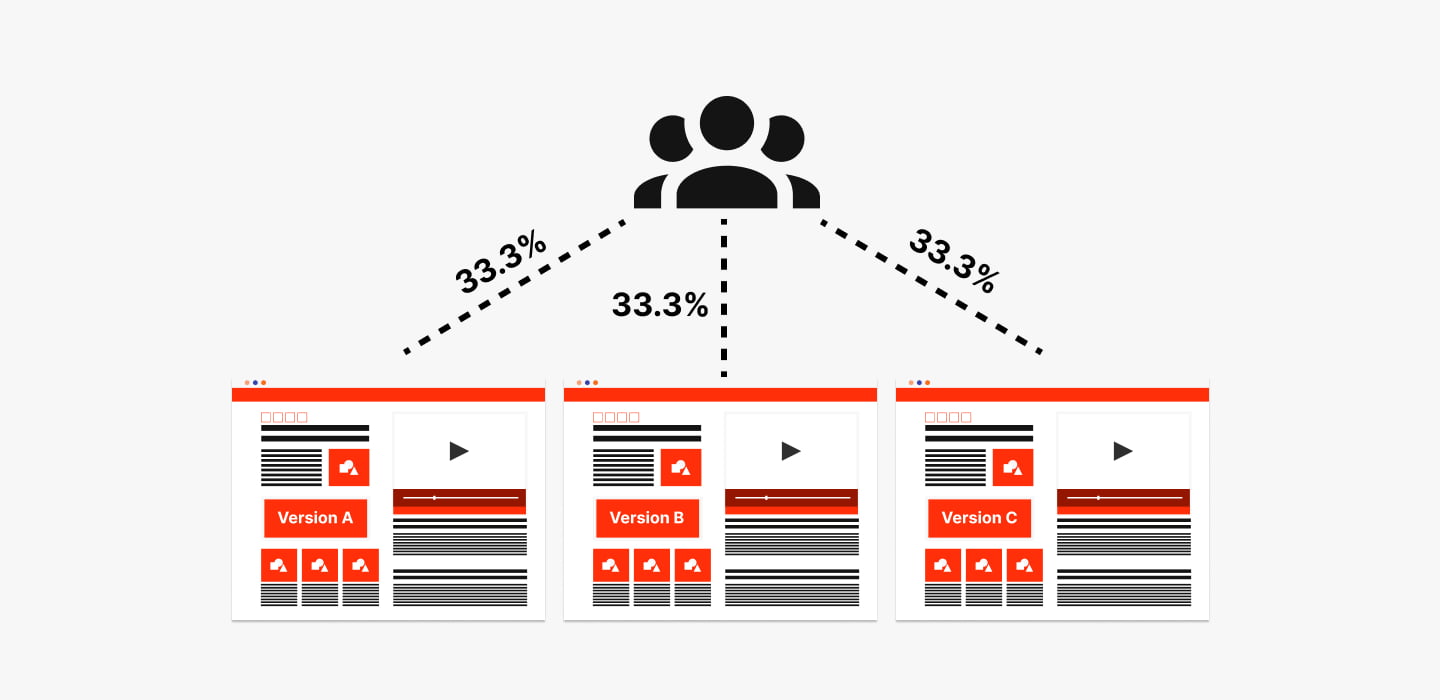
A/B testing is the simplest form of split testing. It involves comparing two variations of a product or website (A and B) to determine which one performs better. A/B testing is often used to test small changes, such as the color of a call-to-action button or the placement of a form on a webpage.
Multivariate testing, also known as MVT, is a more advanced form of A/B testing that involves testing multiple variations at once. This allows for more complex comparisons and can provide more insights about how different elements on a website or product interact with one another.
Multi-page testing, also known as multipage testing, is a form of A/B testing that involves comparing multiple pages on a website to determine which one performs better. This can be useful for testing the effectiveness of landing pages or entire website redesigns.
Setting up A/B/n testing involves several steps:
A/B/n testing has several advantages, including:
While A/B/n testing can be a powerful tool for optimizing a website or product, it does have some limitations, including:
A/B/n testing is a powerful tool for optimizing a website or product for maximum engagement or conversion rates. By randomly showing users different variations of a website or product and measuring their engagement or conversion rates, A/B/n testing allows for data-driven decision making and continuous improvement.
However, A/B/n testing does have limitations, including a limited scope and the need for a large sample size. It also can be time-consuming and may not provide a full understanding of why a change had a particular effect. Overall, A/B/n testing should be used as part of a larger optimization strategy and in conjunction with other methods such as user research and analytics.
A/B/n testing works by randomly showing users one of the variations (A, B, or n) and then measuring their engagement or conversion rate. This is done by using a control group, which is shown the original version of the product or website, and an experimental group, which is shown the variation being tested. The engagement or conversion rate is then compared between the two groups to determine which variation performs better.
A/B testing is the simplest form of split testing. It involves comparing two variations of a product or website (A and B) to determine which one performs better. Multivariate testing (MVT) is a more advanced form of A/B testing that involves testing multiple variations at once. Multi-page testing is a form of A/B testing that involves comparing multiple pages on a website to determine which one performs better.
A/B/n testing has several advantages, including: data-driven decision making, increased engagement and conversion rates, cost-effectiveness, ability to test multiple variations, and continuous improvement.
A/B/n testing has some limitations, such as limited scope, limited insights, sample size, difficulty in identifying the right metric and time-consuming.